
~ Never take any risks when it comes to your server’s security!
While your business will surely offer more and more online services and transactions, internet security becomes both a priority and a necessity for your customers’ online transactions, to ensure that sensitive information – such as a credit card number and personal information – are only being transmitted to legitimate online businesses like yours.
In order to keep customer information private and secure, you will need to add SSL certificates to your website, which are an essential component of the data encryption process that makes internet transactions secure.
In other terms, SSL are digital passports that provide authentication to protect the confidentiality and integrity of website communication with browsers.
The SSL certificate's job is to initiate secure sessions with the user’s browser via the secure sockets layer (SSL) protocol. This secure connection cannot be established without the SSL certificate, which digitally connects company information to a cryptographic key.
What Effect Do SSL certificates Have on Your Business?
There are many benefits to using SSL certificates. Namely, SSL-based websites can:
- Utilize HTTPs, which optimizes SEO and elicits a better rank in the search results of search engines such as Google.
- Create safer experiences for customers, because data they submit is encrypted before it is transmitted through the internet.
- Build customer trust and improve conversions.
- Protect both the customer and internal data.
- Encrypt browser-to-server and server-to-server communication.
- Increase security of your mobile and cloud apps.
Technicalities anyone?
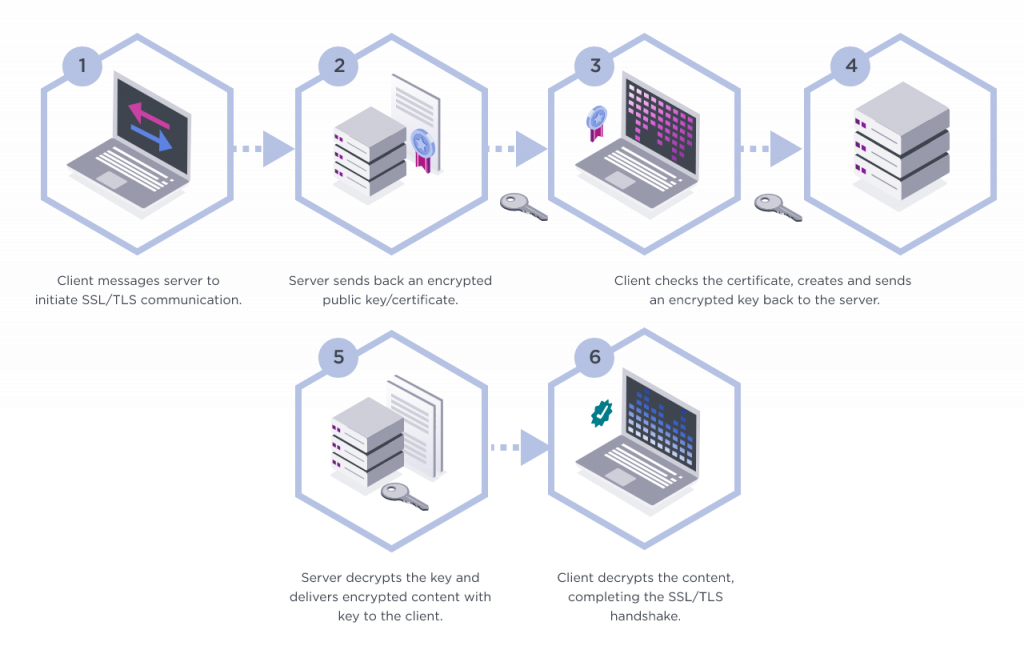
Here is how SSL certificates work:
- A browser or server attempts to connect to a website (i.e. a web server) secured with SSL. The browser/server requests that the web server identify itself.
- The web server sends the browser/server a copy of its SSL certificate.
- The browser/server checks to see whether or not it trusts the SSL certificate.
- If so, it sends a message to the web server.
- The web server sends back a digitally signed acknowledgment to start an SSL encrypted session.
- Encrypted data is shared between the browser/server and the web server.
Self-Signed Certificate vs CA Certificate: What’s the Difference?
When using a self-signed certificate, you’re essentially vouching for your own identity. It’s like writing “I have graduated” on a piece of paper and considering it your official graduation certificate. While you might be excellent in your academics, people aren’t going to trust your self-created certificate! They’d want the document to be issued and signed by an official institution such as a college or university.
In much the same way, no browsers, email clients, or operating systems are going to trust digital certificates that are signed by the entities they’re designed to validate. Hence, why they don’t show any of the above-mentioned trust indicators for self-signed certificates.
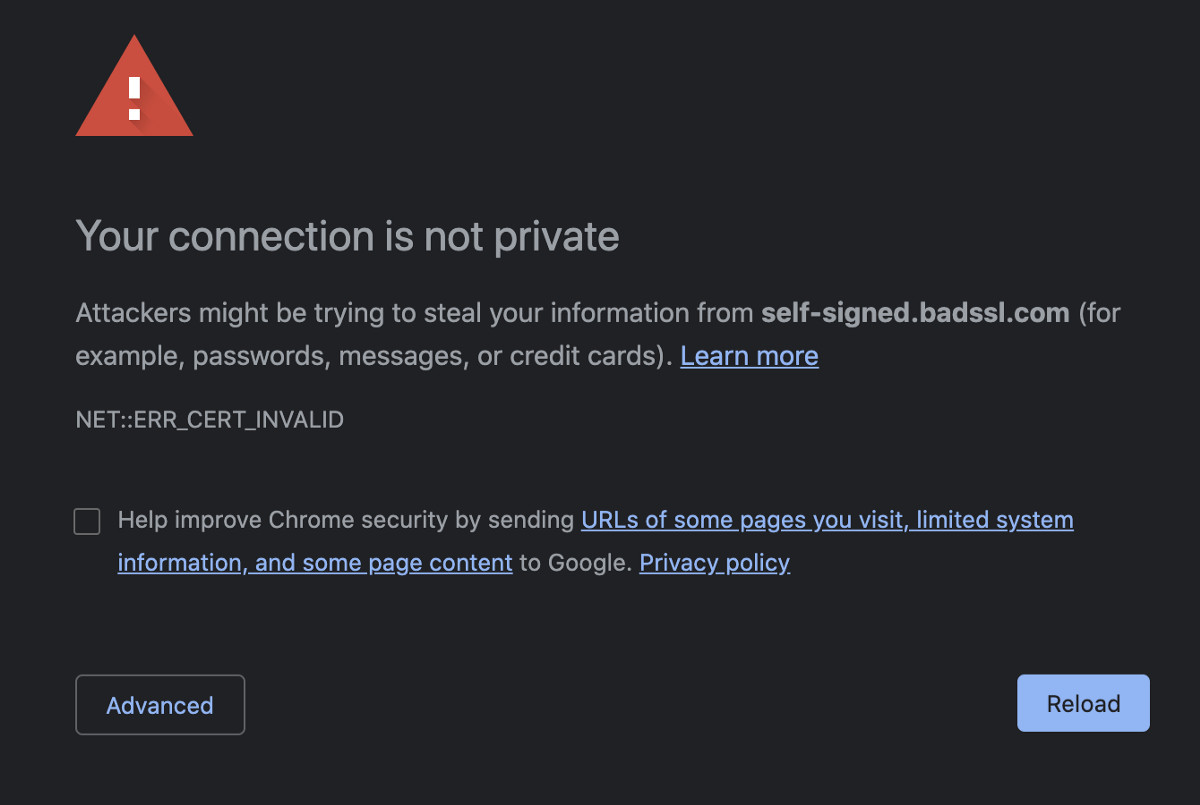
But it gets worse. Not only will browsers not trust a self-signed certificate, but they’ll even display a security warning page with error messages like the one shown below, this means that your website visitors must manually click on the “Accept Risk” button to open your site — and that can drive them away.
The difference between a self-signed and a CA certificate is the issuer of the certificate. A self-signed certificate is created, signed, and issued by the subject of the certificate (the entity it is issued to), while a CA certificate is created, signed, and issued by a third party called a certificate authority (CA) that is authorized to validate the identity of the applicant.
Pros and Cons anyone?
In this next section, we will schematize the pros and cons outlining in a clearer way the real differences between the self-signed and CA certificates.

Advantages of Self-Signed SSL Certificates
- They are free.
- They are very convenient for internal (intranet) sites, and sites used in testing environments.
- You can specify the certificate’s lifetime adding more control over its use.
- Data encryption and decryption are done with the same ciphers used by paid SSL certificates.
Disadvantages of Self-Signed SSL Certificates
- They can cost you more than you think. While you can save some money using a free Self-Signed SSL Certificate at first. There is a high risk that attackers can cause enormous damage to your website, which may be astronomically higher than the price you would pay for an SSL Certificate.
- Their lifetime is manually set upon creation, hence a renewal reminder should be set before they expire, which would cause a management hassle.
- No support for advanced PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) functions (e.g. Online checking of the revocation list etc.).
- They cannot be revoked which makes a compromised certificate difficult to identify, and this has several security challenges.
Couple these self-signed certificate vulnerabilities with the operational challenges most organizations face with expiring and misconfigured certificates, and you can see how attackers can easily exploit this vulnerability.
Advantages of CA Certificates
- They are suitable for all public-facing websites and software.
- They can be revoked by the certificate authority if they discover that it has been compromised, but organizations using self-signed certificates must go through the process of replacing or rotating the certificate.
- They support PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) functions, like:
- SSL/TLS certificates to secure web browsing experiences and communications.
- Digital signatures on software.
- Restricted access to enterprise intranets and VPNs.
- Password-free Wifi access based on device ownership.
- Email and data encryption. - They offer protection and customers’ trust for:
- Paid subscriptions or memberships.
- Tax information, health records of users, or any other personally identifiable information (PII).
- Donations, charity, or fundraising.
- eCommerce facilities.
Disadvantages of CA certificates
- They are paid services. Although there are some free CA certificates such as Let's Encrypt
- You cannot specify the certificate’s lifetime, which is a limiting factor for control freaks.
- You might be led to pay subscriptions for fake and fraudulent CAs... So always make sure that you are purchasing from a trustworthy CA like Symantec, Let's Encrypt, GeoTrust, Comodo, DigiCert, Thawte, GoDaddy, Network Solutions, RapidSSLonline, SSL.com, Entrust Datacard
Bottom Line?
- A self-signed certificate is convenient when used in private networks and testing environments.
- A CA certificate signed by a publicly trusted CA can build trust among website visitors, and therefore, it is used to validate public websites.
How to set up your Self-Signed or CA certificate
Our tech team has prepared a step-by-step tutorial with hands-on examples for securing your site with self-signed or CA certificates on Ubuntu.
Reader Alert
If you feel that this topic is too technical, or beyond your expertise, you can choose a very convenient and practical solution, ready-made, fully tested, and developed by SSD Nodes (That is us 😊) to create a website with an active SSL self-signed certificate.
Just visit our website, choose the server’s specifications that fit your needs, along with any of the 1-Click Applications we offer (WordPress, Zabbix, phpMyAdmin, Webmin, Nextcloud, LAMP, LEMP, Grafana, MongoDB to name a few), complete your checkout, and in a couple of minutes, our algorithms will make it ready to use with an active SSL self-signed certificate!
Enjoy!



One Response to What are SSL Server Certificates and How Do They Protect my Website?
eeeee
nice article