Installing Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu may sound a bit daunting at first, but it's actually pretty easy! Thanks to Certbot, you can quickly install a Let's Encrypt certificate and use it on your Apache and Nginx web servers to secure traffic with SSL/TLS encryption.
In this article, you'll learn how to use the certbot command to install Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu and configure both Apache and Nginx to use HTTPS instead of HTTP.
How to Install Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu
To install Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu with Certbot for Apache and Nginx, first, you'll update your package list. Then, install Certbot and the necessary plugins. Once Certbot is installed, you will use it to generate Let's Encrypt certificate files. Finally, you will set up the certificate in your web server's configuration files.
Prerequisites for Installing Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu
- To follow this tutorial, you'll need an Ubuntu server with sudo privileges. If you haven't noticed, we offer the best priced, most reliable, and fastest Ubuntu servers in the world.
Step 1 - Install Certbot on Ubuntu 24.04
To install certbot and use it with Apache and Nginx on Ubuntu 24.04, first update your package list:
sudo apt updateUse the apt command to install certbot:
sudo apt install -y certbotThis certbot command line tool automates the process of getting and installing a Let's Encrypt certificate valid for 90 days, with the possibility of an automated renewal.
Note
TCP ports 80 (HTTP) & 443 (HTTPS) must be opened on the server firewall for these instructions to work.
Step 2 - Install a Let’s Encrypt Certificate Using Certbot
To create a Let’s Encrypt certificate with certbot on Ubuntu, you’ll use the following command structure:
sudo certbot certonly --webroot --webroot-path WEB_SERVER_ROOT_PATH -m EMAIL -d DOMAIN --agree-tos -nHere is what each part of the preceding command means:
certonly: (certificate only) used to just obtain the certificate without installing it anywhere.--webroot: An option that is used here to keep the web server running while Certbot runs, since we’re already running a local web server, and don't want to stop it during the certificate issuance process.--webroot-pathor-w: Defines the top-level directory (“web root”) containing the files served by your webserver. Note that the web root path must be the path on which files from the domain are served. In our example, it's the web root path from which ourhttp://www.example.comURL serves files.--mailor-m: The email which will be used by the certificate authority to alert you when a domain will expire.--domainor-d: The domain name you’ll use to access the server by.--agree-tos: Confirms our agreement to the ACME server's subscriber agreement.--non-interactiveor-nis used to execute the command without ever asking for user input or prompts.
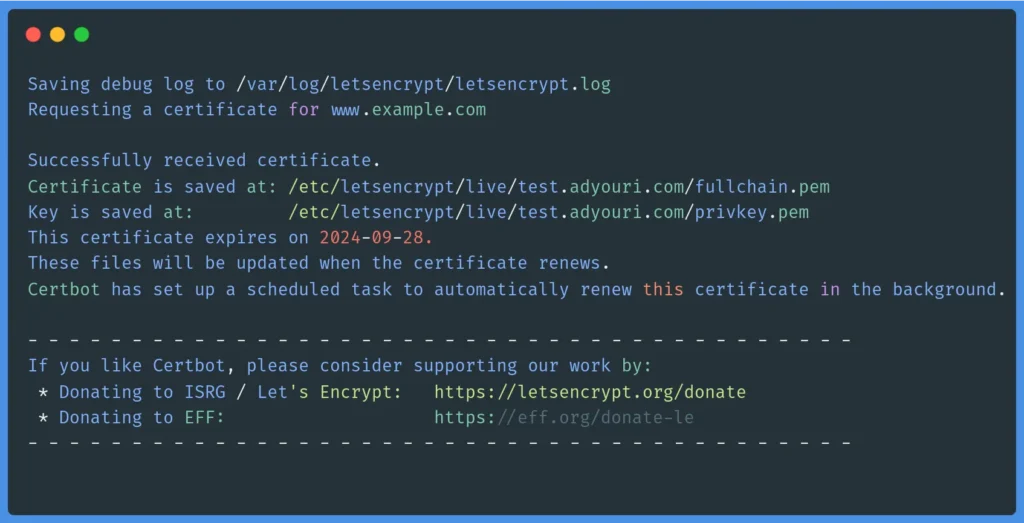
Now that you are familiar with the certbot options and actions, you can form and execute a certbot command to create a certificate. For example, you can use the following command, making sure to set the appropriate values for your case:
sudo certbot certonly --webroot --webroot-path /var/www/html/ -m [email protected] -d www.example.com --agree-tos -nOnce the command is executed, the following two files will be automatically created under the respective subdirectories as follows:
- The private key:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/privkey.pem - The certificate:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/fullchain.pem
Now that you have your Let's Encrypt private key file and your certificate file, you can install your certificate on your web server.
"Only Domain Names Are Supported, Not IP Addresses" Certbot Error
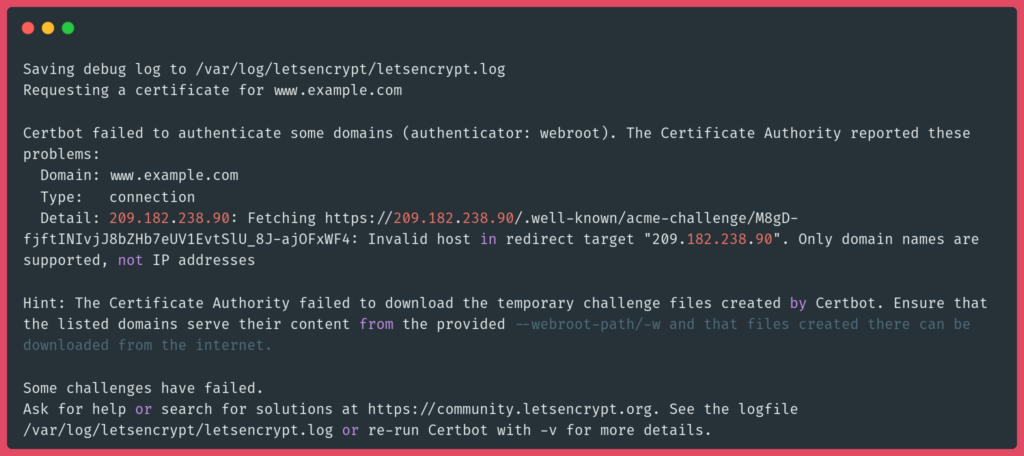
The "Only domain names are supported, not IP addresses" error in Certbot occurs because Let’s Encrypt does not issue SSL certificates for IP addresses. Certificates are only provided for fully qualified domain names (FQDNs). To resolve this, ensure you are using a valid domain name instead of an IP address when requesting a certificate. Register a domain if needed.
Step 3 - Configure An Apache Server with Your Let's Encrypt Certificate
Now that you’ve created a Let’s Encrypt certificate, you can configure your Apache server to use it and enable HTTPS on your website.
First, edit apache’s default configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.confReplace the key and the certificate paths with the Let’s Encrypt private key file and the certificate file (the changes you have to make are highlighted in yellow in the code below):
<VirtualHost *:80>
Define servername www.example.com
ServerName ${SERVERNAME}
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^/.*$ https://\${SERVERNAME}%{SCRIPT_FILENAME}?%{QUERY_STRING} [R=301]
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/privkey.pem
ServerName ${SERVERNAME}
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>Here, you set the SSLCertificateFile directive to the path of the Let’s Encrypt certificate file, and you set the SSLCertificateKeyFile directive to the private key’s path.
Next, test for configuration errors:
sudo apache2ctl configtestYou should receive an output that contains the text Syntax OK, which means you can safely reload Apache, otherwise, you will get a very specific description pointing out the error you have to fix.
Next, restart Apache:
sudo systemctl restart apache2Now, reload your website in the browser. You will notice a secured padlock with a valid certificate message as you can see in the following example, which was taken from the Google Chrome browser:
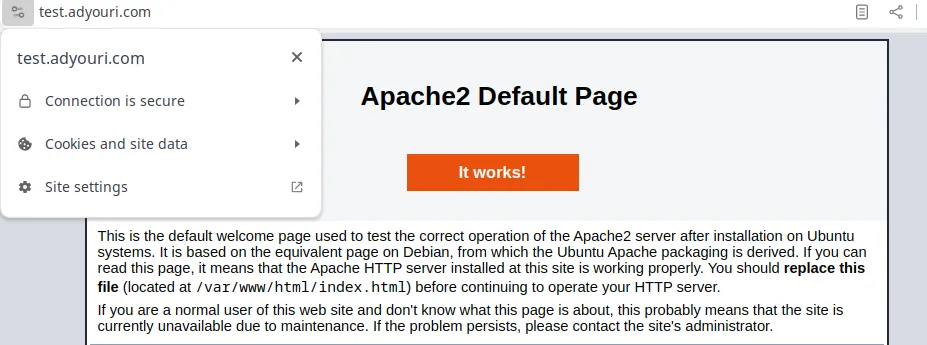
With this, you now have HTTPS enabled in your Apache web server, and you can now secure your web traffic, which establishes customer trust and protects both your internal and public data.
Step 3.2 - Configure an Nginx Server with Your Let's Encrypt Certificate

To configure your Let’s Encrypt certificate with your NGINX server and enable HTTPS on your website. First, edit NGINX’s default configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultReplace the private key and the certificate paths with the Let’s Encrypt private key file and the certificate file generated by Certbot (the changes you have to make are highlighted in yellow in the code below):
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name www.example.com;
access_log off;
location / {
rewrite ^ https://$host$request_uri? permanent;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:443 ssl;
server_name www.example.com;
root /var/www/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
autoindex off;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}Here, you set the ssl_certificate directive to the Let’s Encrypt certificate file path you created earlier, and the ssl_certificate_key directive to the Let’s Encrypt private key file path.
With the configuration file modified, check for syntax errors in it using the following command:
sudo nginx -tThe output should let you know that the configuration file test is successful.
Now, restart NGINX:
sudo systemctl restart nginxReload your browser and you will notice a secured padlock with a valid certificate message as follows:

With this, you now have HTTPS enabled in your NGINX web server, and you can now secure your web traffic, which establishes customer trust and protects both your internal and customer data.
Step 4 - Verifying Your Certificate Information
In the pop-up that comes up when clicking the padlock on the left side of the URL, click on “Certificate is secure” for more details on the CA certificate:
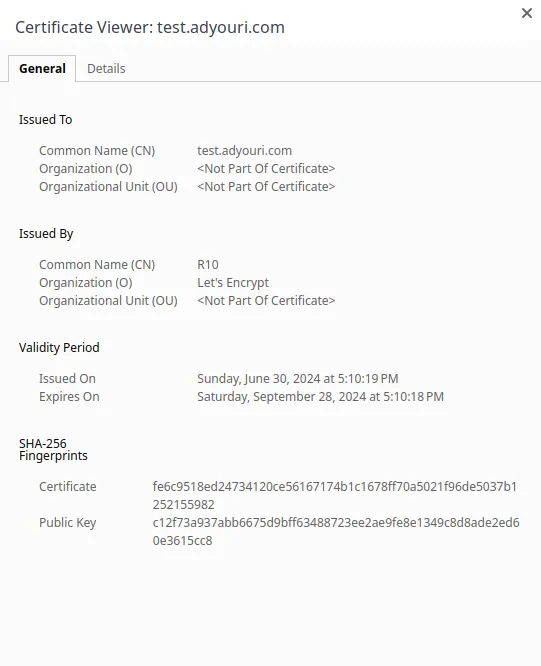
Congrats!
Your Ubuntu server's Apache or Nginx web server has become CA certified with Let's Encrypt, and you can now securely transfer data through HTTPS, and protect your online transactions, and with best security practices, you can handle paid subscriptions, eCommerce orders, memberships, or charity and online fundraising.
Installing a non-Let's-Encrypt CA Certificates
If you are looking to install a non-Let's-Encrypt CA Certificate you'll generally need to do the following:
1) Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
The CSR contains information (e.g. common name, organization, country) which the Certificate Authority (CA) will use to create your certificate. You generate it on the server where you want to install the certificate. It includes the public key that will be part of your certificate, and is signed with the corresponding private key.
Check out How to Create a Self-Signed Certificate, which describes CSR creation for self-signed certificates (which also applies to CA certificates).
2) Upload the CSR to the Certificate Authority (CA)
Please refer to the documentation of the certificate authority of your choice, and follow their instructions to properly upload your certificate signing request, along with any additional information.
Once the CSR is uploaded, the CA replies with your final certificate ready to use.
Let's Encrypt vs Paid SSL
Let's Encrypt provides free SSL certificates. They are automated and easy to set up. Paid SSL certificates offer additional features such as extended validation and warranty. They are suitable for businesses needing higher trust levels. Both encrypt data, but paid SSLs often come with better customer support and additional security features. Choose based on your specific needs.
Is Let's Encrypt Safe?
Yes, Let's Encrypt is safe. It provides the same level of encryption as paid SSL certificates. It is backed by major tech companies and regularly audited for security. Automatic renewals ensure your site stays secure. However, it lacks some advanced features offered by paid certificates. For most websites, Let's Encrypt is a reliable and secure option.
Let's Encrypt Root Certificate Expiring
Let's Encrypt's root certificate expiration is a known issue. Ensure your systems are updated to trust the new root certificate. Older devices might face connectivity issues. Regularly check for updates and ensure compatibility with new certificates. This change is a normal part of maintaining secure encryption. Proper updates will keep your site secure and trusted.
Let's Encrypt Renewals with Certbot
Renewing Let's Encrypt certificates with Certbot is straightforward. Certbot automatically handles renewals for you. By default, it checks for renewal every day and renews certificates that are within 30 days of expiring. Ensure your server is configured to allow automatic renewals. Manual renewal can be done if needed, but automation is recommended for continuous security.
Let's Encrypt Wildcard Certificates
Let's Encrypt offers wildcard certificates, securing multiple subdomains under a single domain. This simplifies certificate management. To obtain a wildcard certificate, use DNS-based domain validation. Ensure your DNS provider supports the necessary API calls. Wildcard certificates are beneficial for sites with numerous subdomains, reducing the need for separate certificates for each one.
A note about tutorials: We encourage our users to try out tutorials, but they aren't fully supported by our team—we can't always provide support when things go wrong. Be sure to check which OS and version it was tested with before you proceed.
If you want a fully managed experience, with dedicated support for any application you might want to run, contact us for more information.




