The internet has changed a lot since its inception. From the early days of static web pages and simple browsers, to the era of social media and user-generated content, to the emerging trends of cryptocurrencies and NFTs, the web has evolved through different phases and technologies. But what is the next phase of the internet? And how will it affect our lives, businesses, and society?
Web3 is being considered a new vision for the internet, one that is based on decentralization, blockchain, and token economics. Web3 aims to create a more open, fair, and secure web, where users have more control over their data, identity, and assets, and where intermediaries and gatekeepers are replaced by peer-to-peer networks and protocols.
But what does Web3 actually mean? How does it work? And why should we care? In this article, we will try to answer these questions in a simple and accessible way. We will explain the basic concepts and features of Web3, its history and development, its advantages and challenges, and some examples of Web3 applications and projects.
Prerequisites
- To fully understand this article, you need to have a basic understanding of the two foundations of Web3: The blockchain and smart contracts. For a comprehensive guide on these two concepts, check out our Beginner's Guide to Blockchain Technology and its Applications.
Web3 for Beginners. Or... Web 1.0 vs Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0
Imagine the internet as a journey through different eras, each bringing unique experiences and opportunities. In this digital voyage, Web 1.0 was like stepping into a library where you could read books but couldn't interact with them or leave your own mark. It was a static and one-sided affair. Fast forward to Web 2.0, and suddenly you find yourself in a bustling marketplace, where you can not only read but also write, share, and engage with others. Web 2.0 introduced social media platforms, blogs, and online communities that turned the internet into a dynamic and interactive space.
Now, as we set sail towards Web3, we find ourselves in a place where everything is like a collective art gallery, a virtual world where you have control, ownership, and the ability to reshape the very fabric of the online landscape. Web3 is driven by technologies like blockchain and decentralized applications, aiming to create a more user-centric and decentralized internet.
To grasp the essence of Web3, consider the analogy of a traditional bank versus a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform. In Web 1.0, accessing financial services meant relying on a central bank, just as browsing websites meant relying on centralized servers. The power was concentrated in the hands of a few, and users had limited control over their financial transactions or online experiences. With the advent of Web 2.0, it was as if you were given the ability to join a credit union or use a peer-to-peer payment app, enabling more user autonomy and interaction. Web2.0 platforms like PayPal and Venmo introduced new possibilities, but they were still reliant on intermediaries.
Enter Web3. Now, envision a financial system where transactions occur directly between individuals through smart contracts, without any intermediaries. This is the promise of decentralized finance powered by Web3. Similarly, in Web3, instead of relying on centralized social media platforms to connect with others and share content, you can engage with decentralized social networks, where you have ownership and control over your data, and where interactions are governed by open protocols rather than closed platforms.
Let's take another analogy: the evolution of film and photography. Web 1.0 was akin to having access to a limited library of photographs, with the ability to view but not edit or contribute to the collection. It was a passive experience, much like browsing static websites. With the rise of Web 2.0, it was as if you entered a world where you could take photos, share them on social media platforms, and even collaborate with others on creative projects. Web 2.0 empowered users to actively participate in the digital imagery landscape.
In the era of Web3, imagine a virtual gallery where you can create, trade, and collect digital art as unique and valuable assets using blockchain technology. Just as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have introduced digital scarcity, Web3 enables the creation and trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which represent digital ownership of unique assets like art, music, and virtual real estate. It's like stepping into an art world where artists can directly connect with collectors and earn royalties from their work, without relying on intermediaries.
Why Does Web3 Matter?
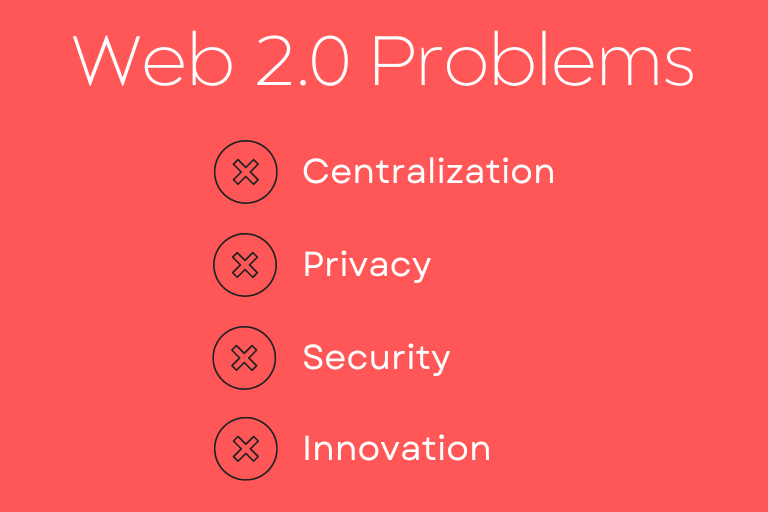
Web3 matters because it offers a new way of building and using the internet that can address some of the problems and limitations of the current Web2 world. Some of these problems include:
- Centralization: The current web is dominated by a few large platforms and companies that have enormous power and influence over the data, content, and services that we use online. These platforms can censor, manipulate, or exploit our data for their own benefit or agenda, without our consent or knowledge. They can also impose fees, restrictions, or rules on how we can access or use their services, limiting our choices and opportunities.
- Privacy: The current web relies on collecting and storing massive amounts of personal data from users, often without their awareness or permission. This data can be used to track, profile, or target users with ads, recommendations, or propaganda. This data can also be leaked, hacked, or sold to third parties without our control or protection. Data can be used against us by governments, corporations, or malicious actors who can spy on us, blackmail us, or discriminate against us.
- Security: The current web depends on trusting third parties to secure our data and transactions online. However, these third parties can be corrupted, compromised, or coerced by hackers, regulators, or competitors who can steal, alter, or destroy our data or assets. These third parties can charge high fees, impose delays, or deny service to users who depend on them for their online activities.
- Innovation: The current web limits the potential for innovation and creativity online. Many platforms and services are closed-source, proprietary, or monopolistic, preventing users from accessing their data or code, modifying their features or functions, or creating new applications or solutions.
Web3 Solutions

Web3 aims to solve the previously mentioned problems by creating a more open, fair, and secure web, where users have more control over their data, identity, and assets, and where intermediaries and gatekeepers are replaced by peer-to-peer networks and protocols. Some of the benefits of Web3 include:
- Decentralization: Web3 enables users to interact directly with each other and with the data and services they need, without relying on centralized platforms or companies. This way, users can avoid censorship, manipulation, or exploitation of their data or content, and enjoy more freedom, choice, and opportunity online. Users can benefit from increased resilience, reliability, and performance of the network, as it does not depend on single points of failure or attack.
- Privacy: Web3 allows users to own and control their own data online, without giving it up to third parties. Users can decide what data they want to share, with whom, and under what conditions, mainly using encryption techniques. Users can also protect their identity and anonymity online, using pseudonyms, or digital signatures. Users can also access their data or services from anywhere, without being tracked, profiled, or targeted by ads.
- Security: Web3 aims to provide users with more security and trust online, without depending on third parties. Users can verify and validate their own data and transactions online, using blockchain , cryptographic technologies, or digital signatures. Instead of relying on banks, users can also secure their own assets online, using cryptocurrencies, digital wallets, or smart contracts. This reduces costs and online risks.
- Innovation: Web3 fosters more innovation and creativity online, as it enables users to access, modify, or create new data, services, or applications online. Users can leverage open-source protocols that allow them to build on top of each other’s work, and customize their own solutions. Web3 users can also increase innovation by incentivizing and rewarding contributions using cryptocurrency.
How Does Web3 Work?
Web3 works by using various technologies and protocols that enable decentralization, blockchain, and smart contracts. Some of these technologies and protocols include:
Ethereum

Ethereum is one of the most popular and influential blockchain platforms that supports Web3 applications and services. Ethereum is a decentralized open-source platform that allows anyone to create and run smart contracts and DApps on its network.
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that encode the rules and logic of an agreement or transaction. DApps are decentralized applications that run on top of smart contracts and provide various functions or services to users.
Ethereum also has its own native cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH) that is used to pay for transactions and computations on its network. For more on smart contracts and DApps, check out our Beginner's Guide to Blockchain Technology and its Applications.
IPFS

IPFS stands for InterPlanetary File System. It is a decentralized protocol that allows users to store and share files across a distributed network of nodes. IPFS aims to create a more efficient, resilient, and permanent web, where files are identified by their content rather than their location.
IPFS also enables users to access files offline, without relying on servers or intermediaries. Unlike Dropbox or Google Drive, which store files in a centralized manner on Google's or Dropbox's servers, IPFS utilizes a distributed network of nodes to store and access files.
NFTs

In the digital world, where information can be easily copied and shared, the concept of owning something unique and scarce seemed elusive. But that all changed with the advent of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs).
Think of NFTs as digital certificates of authenticity, like a virtual Mona Lisa that can't be replicated or replaced. An NFT represents a one-of-a-kind digital asset, whether it's a piece of artwork, a video clip, a tweet, or even a virtual real estate plot in a metaverse. It's a way to establish verifiable ownership and rarity in the digital world.
NFTs have the potential to revolutionize industries and empower creators by solving long-standing challenges in monetizing digital work. Traditionally, artists, musicians, and content creators have struggled to earn fair and transparent compensation for their creations. NFTs offer a solution by enabling direct sales between creators and collectors. An artist can upload their work to a blockchain, convert it into an NFT, and sell it to a global audience.
Web3 Examples
There are already many Web3 examples created and thriving. Some of them are:
OpenSea
OpenSea is a decentralized marketplace for NFTs, where users can buy, sell, and discover digital collectibles, such as art, games, music, domains, etc. OpenSea uses Ethereum and other blockchains to enable users to own and trade their NFTs without intermediaries or fees.
MetaMask
MetaMask is a browser extension and mobile app that allows users to access and interact with Web3 applications and services. MetaMask acts as a bridge between the user’s browser or device and the Ethereum blockchain (or other compatible blockchains). MetaMask also enables users to manage their own identities and accounts, send and receive transactions, sign messages, etc.
Uniswap
Uniswap is a decentralized protocol for exchanging cryptocurrencies and other tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Uniswap uses an automated market maker (AMM) model that allows users to trade tokens without intermediaries or order books. Uniswap also allows users to provide liquidity to the protocol and earn fees from the trading volume.
Aave
Aave is a decentralized protocol that allows users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies and other tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Aave uses smart contracts and interest rate algorithms to enable users to earn interest on their deposits or pay interest on their borrowings. Aave also supports various features and innovations for Web3 users and developers, such as flash loans, credit delegation, liquidity mining, among other things.
Web3 Challenges

Web3 is not without its challenges. There are risks for both consumers and institutional participants.
Web3 Development
Blockchain technology underpins Web3, but it is still a relatively new and complex technology that requires specialized skills and knowledge to develop and deploy. There is a shortage of qualified and experienced developers who can build and maintain Web3 applications and services, as well as a lack of standardized tools, frameworks, and best practices. Bockchain development is often costly, time-consuming, and prone to errors or bugs that can have serious consequences for users and stakeholders.
Interoperability
While Web3 is all about keeping your assets in your wallet rather than entrusting them to a centralized platform, there is one little issue. Different blockchains have different protocols, standards, and features that make them incompatible or difficult to communicate with each other. This limits the potential for cross-chain transactions, collaborations, or innovations among Web3 users and developers. For example, if you have an NFT on Ethereum and want to trade it for another NFT on another blockchain such as Solana, you need to use a bridge or a third-party service that can facilitate the exchange, which may incur fees, delays, or risks.
Scalability
Scalability is a very complicated problem with blockchain technology, and it is a major impediment to Web3 adoption. Scalability refers to the ability of a blockchain network to handle a large number of transactions or users without compromising its speed, security, or cost. However, most blockchains face a trade-off between these factors, as increasing one may decrease the others. For example, Bitcoin can process about 7 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum can process about 15 TPS. These numbers are far from sufficient to support the global demand for Web3 applications and services, especially compared to traditional platforms that can handle thousands of transactions per second. As the demand for blockchain transactions increases, so does the cost of using them, making them unaffordable or impractical for many users.
Conclusion
Web3 represents a future vision for the internet that aims to create a more open, fair, and secure online environment. However, Web3 still faces challenges in many areas, which need to be addressed for its widespread adoption. It is an ongoing process that requires continuous experimentation, collaboration, and improvement. Therefore, it is crucial for business leaders, investors, regulators, and consumers to familiarize themselves with the fundamentals of Web3, its potential applications, impacts, as well as its associated risks and limitations.
A note about tutorials: We encourage our users to try out tutorials, but they aren't fully supported by our team—we can't always provide support when things go wrong. Be sure to check which OS and version it was tested with before you proceed.
If you want a fully managed experience, with dedicated support for any application you might want to run, contact us for more information.

