WordPress + LAMP is the classic web hosting setup.
Sure, there are other software stack options for hosting WordPress (some of our team is partial to LEMP). But in terms of wide implementation and usage for websites across the globe, nothing compares to WordPress with LAMP.
So today we'll show you how to get serve your website to the world by installing WordPress on CentOS 7 using a LAMP stack.
Want to install WordPress but not on CentOs? 👉Click here for our WordPress + Ubunbu 18.04 tutorial 👉Click here for our WordPress + Debian 9 tutorial
WordPress + LAMP: the most popular CMS and web server
WordPress is a powerhouse—over 34% of all websites online today use it—that’s over 22 million websites.
And for sites using a CMS (content management system), it towers over the competition with 60% of the market share.
Meanwhile, Apache (a key piece of the LAMP stack) is the world’s most popular web server.
So, you can see why having the WordPress/LAMP installation in your pocket is key for any developer or anyone looking to host their own blog or website.
How to install WordPress on CentOS 7 using a LAMP stack
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install WordPress with LAMP on Centos 7.
Prerequisites for installing WordPress on CentOS 7
Before we get started, you'll need to have the following set up:
- An instance of CentOS 7
- SSH access to the server
- User with sudo privileges.
- A good internet connection
With all the prerequisites in place, let’s dive in!
The latest version of WordPress requires PHP 7.3 or later, so you'll need to install the Remi repository first.
To achieve this, execute the command:
$ sudo yum -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
By default, CentOS 7 ships with PHP 5.4 which is no longer supported by developers and isn't compatible with the latest WordPress version (WordPress 5.2.2). So you'll need to disable PHP 5.4 using the yum config manager which is provided by the yum-utils tool.
To do this, first, install yum-utils package.
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
Next, disable PHP 5.4.
$ sudo yum-config-manager --disable remi-php54
And now enable PHP 7.3 as shown.
$ sudo yum-config-manager --enable remi-php73
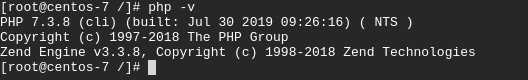
To verify that you have PHP 7.3 installed in your system, run the following command.
$ php -v
Sample output:
Step 2: Install LAMP
The latest version of WordPress requires PHP 7.3 or later, so you'll need to install the Remi repository first.
To achieve this, execute the command:
$ sudo yum -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
By default, CentOS 7 ships with PHP 5.4 which is no longer supported by developers and isn't compatible with the latest WordPress version (WordPress 5.2.2). So you'll need to disable PHP 5.4 using the yum config manager which is provided by the yum-utils tool.
To do this, first, install yum-utils package.
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
Next, disable PHP 5.4.
$ sudo yum-config-manager --disable remi-php54
And now enable PHP 7.3 as shown.
$ sudo yum-config-manager --enable remi-php73
To verify that you have PHP 7.3 installed in your system, run the following command.
$ php -v
Sample output:

Step 2: Install LAMP
by subscribing to our newsletter.
A note about tutorials: We encourage our users to try out tutorials, but they aren't fully supported by our team—we can't always provide support when things go wrong. Be sure to check which OS and version it was tested with before you proceed.
If you want a fully managed experience, with dedicated support for any application you might want to run, contact us for more information.




