Managing servers through web dashboards works fine when you have one or two machines. But once you're dealing with multiple environments, client projects, or complex deployment workflows, clicking through interfaces becomes a massive time sink.
The SSD Nodes VPS API changes this completely. Instead of manual server management, you get programmatic control over your existing VPS infrastructure. No more logging into dashboards to restart servers, check snapshots, or reinstall operating systems.
The VPS API works with your current infrastructure. So that you can automate everything from development workflows to emergency recovery procedures using the servers you already own.
Understanding What the VPS API Actually Does
For just $2/mo, the SSD Nodes API gives you complete control over existing servers through simple HTTP requests. You can check server status, reinstall operating systems, manage snapshots, control power states, and handle authentication. All through code.
The authentication uses bearer tokens that you generate once in your dashboard. These tokens work with standard REST endpoints that return clean JSON responses.
Our rate limits are generous enough for production use: 2000 requests per day, 100 per hour, and 5 per minute.
What’s more, most operations complete quickly, but reinstalls take 5-10 minutes depending on the operating system or application you're deploying.
The API also provides clear status messages so you know exactly what's happening.
The SSD Nodes API includes endpoints for complete server lifecycle management:
- Server discovery and status checking
- Operating system and 1-Click app deployment
- Snapshot management and restoration
- Power state control (start, stop, restart)
- Authentication management (password resets, console access)
VPS API Use Case # 1 - Fresh Environment Factory

One of the most powerful patterns is using reinstalls combined with custom setup scripts. This creates a "fresh environment factory" where you can get guaranteed clean setups in minutes.
Here's how it works: reinstall a server with your preferred OS, SSH in automatically, run your setup script, do your work, then reinstall again when you're done. Each cycle gives you a completely fresh environment without configuration drift or leftover files.
We've seen development teams use this for testing deployment scripts. They reinstall a server with fresh Ubuntu, run their deployment automation, and see exactly what happens on a clean system. If something breaks, they just reinstall and try again.
# Reinstall server with Ubuntu 24.04
curl -X POST https://api.ssdnodes.com/servers/1234/reinstall \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"reinstall_type":"os","os_app_id":1663,"authentication":"ssh","ssh_key":"ssh-rsa AAAAB3..."}'
Take a look at the documentation for a full explanation of the above request.
The real power comes from combining this with your own automation. After the reinstall completes, your scripts can SSH in and configure everything exactly how you need it.
Practical Implementation
A typical fresh environment workflow looks like this:
- Trigger reinstall through the API with your preferred OS or 1-Click app
- Wait for completion (5-10 minutes depending on the installation)
- SSH into the fresh system using your pre-configured keys
- Run your setup scripts to install dependencies and configure applications
- Do your work (testing, development, demos)
- Reinstall again when you need a clean slate
This pattern works incredibly well for agencies switching between client projects. Finish one client's work, reinstall the server, deploy the next client's environment. Each project gets a completely isolated, clean setup.
Your deployment scripts run against the exact same environment every time. No worrying about leftover configuration files, installed packages, or modified system settings affecting your new deployment.
Development teams use this for testing complex deployment procedures. Instead of wondering if their automation works on fresh systems, they can test it repeatedly on actually fresh systems. Each test cycle gets a completely clean installation with one of our supported distros.
VPS API Use Case # 2 - Development Time Machine with Snapshots
Snapshots turn your servers into time machines. The API lets you create restore points before making changes, experiment freely, then roll back if something goes wrong.
The snapshot workflow is simple: check what snapshots exist, do your risky work, then restore if needed. Since snapshots include both daily automated backups and on-demand saves, you have multiple restore points to choose from.
# List available snapshots
curl -X GET https://api.ssdnodes.com/servers/1234/snapshots \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN"
# Restore a snapshot
curl -X POST https://api.ssdnodes.com/servers/1234/restore-snapshot \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"snapshot_name":"20250502_daily"}'
Development teams can use this for testing major updates or system changes. They can snapshot their working environment, apply the update, test everything, then either keep the changes or restore to the snapshot. No stress about breaking things permanently.
Advanced Snapshot Strategies
The most effective teams develop sophisticated snapshot strategies that go beyond simple backup and restore:
Golden State Management: Create snapshots of perfectly configured environments for different purposes. One snapshot might contain a fully configured development environment with all tools installed. Another might have a clean LAMP stack ready for new projects.
Experiment Branching: Before trying risky configuration changes or software updates, create a snapshot. If the experiment succeeds, keep the changes. If it fails, restore to the snapshot and try a different approach. This enables aggressive experimentation without fear of breaking working systems.
Regression Testing: Maintain snapshots from different points in your project timeline. When bugs appear, you can quickly restore to earlier versions to identify when problems were introduced.
This can be especially valuable when you're experimenting with server configurations or trying new software stacks. You can be aggressive with testing because you know you can always get back to a working state.
The time savings add up quickly. Configuring a complex development environment from scratch might take hours. Restoring from a snapshot takes minutes.
VPS API Use Case # 3 - Automated Emergency Response and Monitoring
When things break at 2 AM, you want automated recovery, not emergency manual work. The API enables sophisticated incident response workflows that can detect problems and fix them automatically.
The most common pattern combines monitoring with automatic snapshot restoration. If your monitoring detects a critical failure, your scripts can restore to the last known good state and notify your team.
# Emergency restore to latest snapshot
curl -X POST https://api.ssdnodes.com/servers/1234/restore-snapshot \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"snapshot_name":"20250507_daily"}'
# Reset root password for emergency access
curl -X POST https://api.ssdnodes.com/servers/1234/reset-root-password \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN"
VPS API Use Case # 4 - Server Health Monitoring and Status Management
The API provides detailed server information that integrates perfectly with monitoring systems. Instead of checking dashboards manually, your monitoring tools can query server status automatically.
# Get detailed server information
curl -X GET https://api.ssdnodes.com/servers/1234 \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN"
Server details include current state, IP addresses, resource allocation, and console status. This data can feed into your dashboards, alerting systems, and capacity planning tools.
The response includes everything you need for monitoring:
- Current power state (running, stopped, etc.)
- IP address and network configuration
- Memory, CPU, and disk allocation
- Operating system information
- Console access status
Your monitoring systems can track this data over time to identify patterns. Servers that restart frequently might indicate hardware issues. Resource usage trends help with capacity planning. Console access status ensures emergency access remains available.
The real value comes from automating responses to status changes. If a server stops unexpectedly, your monitoring can automatically restart it and alert your team. No manual intervention required for common issues.
Building Your API Integration
Starting with the SSD Nodes API is straightforward.
Generate an access token in your dashboard:
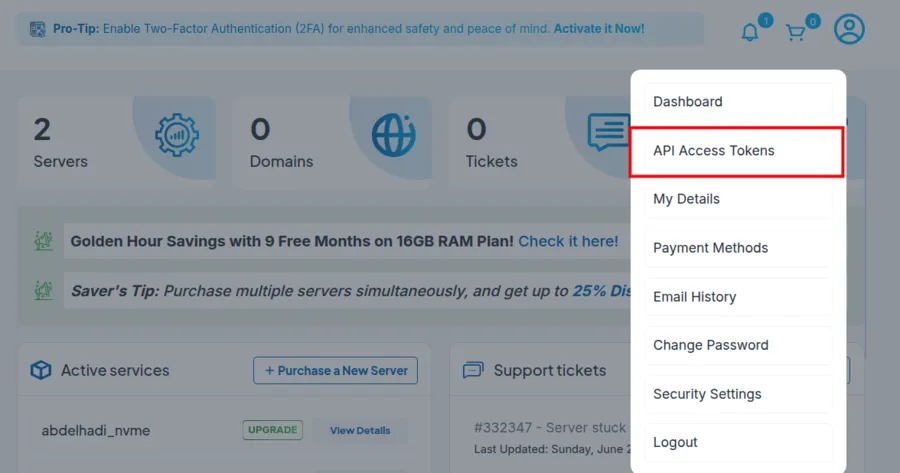
Then begin with simple read operations to understand the response formats.
List your servers first to see what you're working with.
Check server details to understand the data structure.
Look at available snapshots to see backup options. These read operations help you understand your current infrastructure before building automation.
The write operations require more planning.
Test reinstalls on development servers before automating production changes. Then work on understanding how long operations take so your scripts wait appropriately.
Refer to the API documentation for detailed instructions.
Error handling is critical for VPS automation
The SSD Nodes API does provide very clear error messages by default, but your scripts need to handle various failure scenarios.
This is also where using API contract testing tools becomes valuable, because they help validate that each API response structure remains consistent as you automate more workflows.
Network timeouts, invalid server states, and quota limits all require appropriate responses just in case something goes wrong with your operations.
VPS API Best Practices
Authentication tokens should be stored securely and rotated regularly. Don't hardcode them in scripts or store them in plain text.
Remember to use environment variables or secure credential management systems.
Operation timing varies based on server load and operation complexity.
Note that reinstalls usually take 5-10 minutes, but can be longer during peak times. You also ideally want to build appropriate timeouts and retry logic into your automation.
The API works reliably, but your automation should handle edge cases gracefully. Servers sometimes take longer to respond after power state changes.
Network connectivity issues can also cause temporary failures. Good automation handles these situations without breaking.
Warning: Server state management requires coordination between different automation systems. If multiple scripts control the same servers, they need to coordinate or conflicts will occur.
Getting Started With Real VPS Automation
The SSD Nodes API transforms server management from manual work to automated operations. Make sure to start simple with read-only operations to understand your infrastructure, then gradually add automation for common tasks.
Focus on solving actual problems rather than building complex systems immediately. If you're spending time manually restarting servers, automate that first.
If environment setup takes too long, build standardized deployment automation with tools like Ansible.
The API documentation provides working examples for every endpoint. Use these as starting points, then modify them for your specific needs. Test everything on development servers before automating production operations.
Remember that good automation reduces work over time, but requires upfront investment to build correctly. Plan your integrations carefully, handle errors gracefully, and monitor operations to ensure everything works as expected.
Your existing servers become much more valuable when you can control them programmatically. Manual management doesn't scale, but API automation does.